Page
1, 2

ECE Compound Dieckol
Newly discovered class of polyphenols extracted from the Ecklonia cava seaweed,
collectively called ''ECE.'' Two of ECE's more
than 13 active fractions (dieckol and PFF) that are particularly important
are provided in Figures 10 and 11.
Figure 10: Dieckol Structure
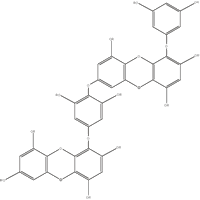
ECE Compound phlorofuro-fucoeckol (PFF)
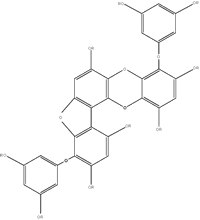
The ECE compound phlorofurofucoeckol (PFF) has a very complicated molecular
structure and a doubling of the rings, which explains its powerful antioxidant
activity (Figure 11). When combined with a much longer in vivo effect, ECE'S
free radical scavenging ability is ten to 100 times more powerful than land-based
polyphenols, far exceeding resveratrol and green tea catechins.
Figure 11: PFF Structure
Fat-Soluble Polyphenol
Water-soluble compounds have less ability to penetrate the blood brain barrier.
ECE compounds are 40% lipid soluble (i.e., "hydrophobic"). This
means ECE has the ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, implying
greater ability to get into and protect the brain. It also means a much longer
half-life in the body, up to 12 hours compared to 30 minutes for most water-soluble
polyphenols. The difference in half-life is considered to be one of a few
key factors in determining its enhanced antioxidant effects.
ACE Inhibition
ECE compounds can potently suppress Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE). In
a rat study, the renal artery was clipped, stimulating the organ to make
the hormone rennin, which in turn stimulates ACE to increase blood pressure.
ECE was compared to the drug enalapril (Vasotec); it showed a similar blood
pressure-lowering profile. But unlike the rats given the drug, ECE rats did
not show the rebound in blood pressure when the product was stopped. ECE
has more than 15 times the power to inhibit ACE as the most powerful land-based
polyphenols.
ECE Comparable to Viagra®
Nitric oxide (NO) dilates blood vessels. After six weeks of ECE treatment,
flow-mediated dilation and NO-mediated dilation increased by 60% and 50%,
respectively. This means ECE can rejuvenate damaged endothelial cells. This
effect was further confirmed in a study on erectile dysfunction (ED). In
an eight-week study on 31 men with ED for more than six months, ECE was compared
with the drug Viagra® in the following parameters: orgasmic function,
intercourse satisfaction, overall satisfaction, and erectile dysfunction.
ECE scored 87%, 74%, 62%, and 66%, respectively. Viagra® scored 27%,
44%, 39%, and 66%, respectively. No side effects were reported.
Neuropathy
The strong lipid and cholesterol scavenging potential of ECE to "scrub" the
endothelial lining of plaque in the blood vessels and arteries provides a further
additional benefit: reduced vasculitis (i.e., vascular inflammation). Increasingly,
the scientific literature supports the notion that many forms of nerve pain
(''neuropathy") are caused by nerve pressure, as exerted
by swollen, inflamed blood vessels adjacent to the nerves. A recent 40-patient,
placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial on neuropathy confirmed ECE's
ability (''NeuralPlus®") to reduce nerve pain by 40%
in four weeks of daily dosing, with an 80% response rate.
Brain Support
Dr. Lee's study found that the velocity of blood flow into the carotid
arteries can be increased from an average of 36.68 cm/sec. to 40.09 cm/sec,
while the placebo group had no improvement. An EEG study on brain waves of
healthy, middle-aged volunteers found that ECE compounds increase alpha waves,
an indicator of relaxation. Yet another study found that ECE compounds prevented
sleepiness in bus drivers and in high school students during daytime activities.
Asthma, Allergic Lung Disease, and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
In a mouse study, Dr. Lee's team found that allergic inflammation was
significantly reduced. Specifically, the migration of eosinophils to the lungs
was reduced by 75%; inflammatory white blood cells were reduced by 50%; mucus
plug in airways was reduced by 50%; the increase in number of airway epithelial
(lining) cells was reduced by 75%; and collagen (fibrosis) in lung tissue and
smooth muscle cell thickness was reduced by 20% and 32%, respectively. These
latter findings suggest that ECE compounds can prevent or reverse the chronic
progression of asthma and potentially even Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
(COPD).
Arthritis, Pain, and Atherosclerosis
ECE significantly reduced pain in a group of knee arthritis patients compared
with placebo. Oxygenase enzymes called LOX (lipo-oxygenase) are related to
the generation of allergies, atherosclerosis, and some cancers. ECE compared
almost identically to celecoxib (Celebrex) in the ability to reduce PGE2
by slowing down the LOX system. Its compounds have more than double the ability
of resveratrol to inhibit LOX. The benefit was demonstrated in a study on
rabbit cartilage cells. Those cells fed ECE had up to an 80% reduction in
degeneration.
Sleep and Alertness
Considering the improvement in sleep for fibromyalgia patients and the increased
alertness for high school students and bus drivers, ECE appears to be stimulating
ideal function: increased alertness when you need it and increased ability
to sleep when you need it. The more than 50 million Americans with various
sleep disorders might well benefit from ECE, without the fears of addiction
present with prescription sleep aids.
Radiation and Cancer Protection
Dr. Lee conducted a study on the effects of ECE compounds on mice exposed to
UV rays. Mice were given either oral or topical ECE and then exposed to UVB,
a toxic ultraviolet wavelength. The results were remarkable. Tumor cell division
was reduced by 50%. The inflammatory chemical PGE2 was reduced by 50-80%.
COX2 and other inflammatory enzymes were significantly reduced.
Inhibitor of Aldose Reductase
High blood sugar leads to vascular complication. One way that happens is through
an enzyme called aldose reductase (AR). This enzyme is present in the eyes,
nerves, and many other parts of the body. It becomes dangerous when blood
sugar gets too high. It converts some of the excess glucose into the sugar
alcohol sorbitol. Sorbitol can build up in these critical cells and damage
them. In fact, recent research found that animals deficient in AR were protected
from the retinal complications of diabetes. ECE compounds are potent inhibitors
of this enzyme. Hence, patients with metabolic syndrome, syndrome X, or frank
diabetes, would benefit from ECE.
Obesity
ECE might naturally prevent fat accumulation. In a mouse study, ECE inhibited
diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT), reduced blood sugar, reduced fat cells
and fat resorption, and decreased the number of fat cells during the feeding
period. ECE induced a 30% reduction in blood vessels to fat tissue [angiogenesis]
and significantly reduced lipid contents in skeletal muscles and around blood
vessels. Obese mice lost more than ten percent of their body weight in 120
days. The animals suffered no side effects, had shiny skin, and were more
active and alert.
Reduced Fat, Increased Muscle
ECE compounds can inhibit DGAT more than 50%. In mice, suppressing DGAT led
to reduced body fat and increased physical activity. But most important,
it encouraged leanness in animals and resistance to a high fat diet. One
hundred and forty-one young adults were given a beverage containing ECE at
a daily dose of 200mmg/D. In just two weeks, average weight dropped over
1.09kg, muscle mass increased over 1.13kg, and body fat dropped 1.86kg. Body
fat in this group dropped a stunning and highly statistically significant
7.48%. ECE blocks fat creation and stimulates its combustion via increase
in muscle mass.
Reduced Fat in Liver and Pancreas
A mouse study showed that ECE reversed fat deposition in liver and pancreas
cells. Furthermore, this same study showed that ECE served to markedly inhibit
Nf-kB inflammation in the pancreas. A recent Harvard (Joslin School of Diabetes)
mouse study directly implicates excessive fat deposition in the mouse pancreas
as turning on the Nf-kB inflammation pathway, resulting in full-blown type
2 diabetes and insulin insensitivity in the mice. It makes sense that a substance
that reduces pancreas fat accumulation might restore insulin production and
reverse type 2 diabetes.
Atherogenic Index Drop
If insulin metabolism is impaired, lipid and cholesterol metabolism will also
be impaired. Thirty-nine adults average age 55.6 were given 100 mg ECE compounds
for six weeks. Their average cholesterol dropped from 228 to 224. LDL dropped
from 141 to 135; HDL rose from 46.5 to 50.7 (highly significant); triglycerides
fell from 215 to 195; and the atherogenic index dropped 12.5%. Although some
of these individual changes were quite moderate, all were in a therapeutic
direction. These results were achieved with no changes in lifestyle.
Summary of ECE
•
Uniquely strong antioxidant scavenging of lipids, calcium, iron, and
cholesterol as well as "free radicals" from the cardiovascular
system (thereby lowering risk of stroke and cardiovascular events,
lowering cholesterol levels, and reducing vasculitis-associated neuropathy)
• Strong anti-plasmin inhibition effect (i.e., enhances blood flow, thereby
lowering blood pressure and increasing arterial blood flow)
• Strong elastase agonist effect, thereby increasing the flexibility
of the vascular system and helping normalize blood flows and blood
pressure
• Significant anti-inflammatory effect, by inhibition of the Nf-kB inflammatory
pathway, which also serves to normalize blood glucose levels and lead
to statistically-significant re-establishment of insulin sensitivity
in the pancreas
• Downregulation (by 60%) of the DGAT enzyme responsible for lipid (fat)
metabolism, thereby assisting in fat/weight loss
• Significant analgesic effect in inhibiting the expression of the COX
enzymes for arthritis, as well as for neuropathic and FMS/CFS pain
• Inhibition of beta-amyloid brain plaque formation as well as short-term
memory in mammals, thereby improving overall memory function
• Anti-tumor effects (currently tested only for dermatologic cancers
in mice)
Summary of Clinical Studies
• Hypertensive cardiovascular patients (reduction of blood pressure and
increase of brachial artery FMD [+43%] and NMD [+59%] in CAD patients
[11 of 39 patients, the others being healthy normals]
• Analgesia in osteoarthritic patients (comparable to the COX-2 inhibitors)
• Weight loss in both obese and normal patients
•
Erectile dysfunction on males with ED (comparable to Viagra®)
• Analgesia in neuropathic pain patients (i.e., neuralgia)
• Major multi-symptom management (i.e., reduction in pain, fatigue, sleep
disorders) for fibromyalgia patients.

References
General
Chapman VJ, Chapman DJ. Seaweeds and Their
Uses. London: Chapman & Hall;
1980.
Glombitza KW, Gerstberger G. Phlorotannins with dibenzodioxin structural
elements from the brown alga eisenia arborea. Phytochemistry. 1985;24:
543-551.
Hoppe HA. Marine algae and their products and constituents in pharmacy.
In: Marine Algae in Pharmaceutical Science. Hoppe HA, Levring T,
Tanaka Y, eds. Berlin & New York: Walter de Gruyter; 1979.
Antioxidant Function
Athukorala Y, Kim KN, Jeon YJ. Antiproliferative and antioxidant properties
of an enzymatic hydrolysate from brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Food
Chem Toxicol. 2006 Jul;44(7):1065-74. Epub 2006 Mar 3.
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Zhang R, Jung MS, Ham YM, Baik JS, Lee NH,
Hyun JW. Cytoprotective effect of phloroglucinol on oxidative stress
induced cell damage via catalase activation. J
Cell Biochem. 2006 Feb
15;97(3):609-20.
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Zhang R, Jung MS, Lee Y, Kim SY, Kim HS, Joo
HG, Park JW, Ham YM, Lee NH, Hyun JW. Eckol isolated from Ecklonia
cava attenuates oxidative stress induced cell damage in lung fibroblast
cells. FEBS Lett. 2005 Nov 21;579(28):6295-304. Epub 2005 Oct 19.
Kang KA, Zhang R, Lee KH, Chae S, Kim BJ, Kwak YS, Park JW, Lee NH,
Hyun JW. Protective effect of triphlorethol-A from Ecklonia cava against
ionizing radiation in vitro. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 2006 Mar;47(1):61-8.
Kang K, Park Y, Hwang HJ, Kim SH, Lee JG, Shin HC. Antioxidative properties
of brown algae polyphenolics and their perspectives as chemopreventive
agents against vascular risk factors. Arch.
Pharm. Res. 2003;26: 286-293.
Kang KJ, Hwang HJ, Hong DH, Park YJ, Kim SH, Lee BH, Shin HC. "Anti-Oxidant
and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ventol, A Phlorotannin-Rich Natural
Agent Derived From Ecklonia Cava, and Its Effect on Proteoglycan Degradation
in Cartilage Explant Culture." Submitted to Molecular
Pathology And Pharmacology.
Nakamura T, Nagayama K, Uchida K, Tanaka R. Antioxidant activity of
phlorotannins isolated from the brown alga eisenia bicyclis. Fisheries
Sci. 1996;62: 923-926.
Allergies/Asthma
Aikawa T, Shimura S, Sasaki H, Ebina M, Takishima T. Marked goblet
cell hyperplasia with mucus accumulation in the airways of patients
who died of severe acute asthma attack. Chest. 1992;101:916-921.
Djukanovic R, Wilson JW, Britten KM, Wilson SJ, Walls AF, Roche WR,
Howarth PH, Holgate ST. Quantitation of mast cells and eosinophils
in the bronchial mucosal of symptomatic atopic asthmatics and healthy
control subjects using immunohistochemistry. Am.
Rev. Respir. Dis.
1990;142:863-871.
Grunig G, Warnock M, Wakil AE, Venkayya R, Brombacher F, Rennick DM,
Sheppard D, Mohrs M, Donaldson DD, Locksley RM, Corry DB. Requirement
For Il-13 Independently Of Il-4 In Experimental Asthma. Science. 1998;282:2261-2263.
Henderson WR, Chi EY. Ultrastructural characterization and morphometric
analysis of human eosinophil degranulation. J.
Cell Sci. 1985;73:33-48.
Henderson WR, Jr., Lewis DB, Albert RK, Zhang Y, Lamm WJE, Chiang GKS,
Jones F, Eriksen P, Tien Y, Jonas M, Chi EY. The importance of leukotrienes
in airway inflammation in a mouse model of asthma. J.
Exp. Med. 1996;184:1483-1494.
Henderson WR, Jr., Chi EY, Maliszewski CR. Soluble interleukin-4 receptor
(sil-4r) inhibits airway inflammation following allergen challenge
in a mouse model of asthma. J. Immunol. 2000;164:1086-1095.
Hoshino M, Nakamura Y, Sim JJ. Expression of growth factors and remodeling
of the airway wall in bronchial asthma. Thorax. 1998;53:21-27.
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Koh YS, Yoo BS, Kim JH, Ham YM, Baik JS, Lee
NH, Hyun JW. Triphlorethol-A from Ecklonia cava protects V79-4 lung
fibroblast against hydrogen peroxide induced cell damage. Free
Radic Res. 2005 Aug;39(8):883-92.
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Zhang R, Jung MS, Lee Y, Kim SY, Kim HS, Joo
HG, Park JW, Ham YM, Lee NH, Hyun JW. Eckol isolated from Ecklonia
cava attenuates oxidative stress induced cell damage in lung fibroblast
cells. FEBS Lett. 2005 Nov 21;579(28):6295-304. Epub 2005 Oct 19.
Krug N, Madden J, Redington AE, Lackie P, Djukanovic R, Schauer U,
Holgate ST, Frew AJ, Howarth PH. T-cell cytokine profile evaluated
at the single cell level in bal and blood in allergic asthma. Am.
J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996;14:319-326.
Kay AB. T cells as orchestrators of the asthmatic response. Ciba
Found. Symp. 1997;206:56-67.
Roche WR, Beasley R, Williams JH, Holgate ST. Subepithelial fibrosis
in the bronchi of asthmatics. Lancet. 1989;1:520-524.
Temann UA, Prasad B, Gallup MW, Basbaum C, Ho SB, Flavell RA, Rankin
JA. A novel role for murine il-4 in vivo: induction of muc5ac gene
expression and mucin hypersecretion. Am. J.
Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997;16:471-478.
Wills-Karp MJ, Luyimbazi, Xu X, Schofield B, Neben TY, Karp CL, Donaldson
DD. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science. 1998;282:2258-2261.
Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, Chen Q, Geba GP, Wang J, Zhang Y, Elias JA.
Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion,
subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production.
J. Clin. Invest. 1999;103:779-788.
Cardiovascular Support
"Compound For Improving Hypertension Containing Inhibitors Of Angiotensin
Converting Enzyme Activity Extracted From Marin Plants And Articles
Comprising Thereof." Korean Patent Application 10-2004-24347
(Livechem, Inc)
Fukuyama Y, Kodama M, Miura I, Kinzyo Z, Kido M, Mori H, Nakayama Y,
Takahashi M. Structure of an anti-plasmin inhibitor, eckol, isolated
from the brown alga ecklonia kurome okamura and inhibitory activities
of its derivatives on plasmin inhibitors. Chem.
Pharm. Bull. 1989;37:
349-353.
Fukuyama Y, Kodama M, Miura I, Kinzyo Z, Mori H, Nakayama Y, Takahashi
M. Anti-plasmin inhibitor. vi. structure of phlorofucofuroeckol a,
a novel phlorotannin with both dibenzo-1,4-dioxin and dibenzofuran
elements, from ecklonia kurome okamura. Chem.
Pharm. Bull. 1990;38:
133-135.
Uhm CS, Kim KB, Lim JH, Pee DH, Kim YH, Kim H, Eun BL, Tockgo YC. Effective
treatment with fucoidin for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
in rats. Neuroscience Letters. 2003;353: 21-24.
Kang K, Park Y, Hwang HJ, Kim SH, Lee JG, Shin HC. Antioxidative properties
of brown algae polyphenolics and their perspectives as chemopreventive
agents against vascular risk factors. Arch.
Pharm. Res. 2003;26: 286-293.
Ruehl ML, Orozco JA, Stoker MB, Mcdonagh PF, Coull BM, Ritter LS. Protective
effects of inhibiting both blood and vascular selectins after stroke
and reperfusion. Neurol Res. 2002 Apr;24(3):226-32.
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile and endothelial dysfunction in type ii diabetes-a possible
link. Diabetologia. 2001;44: 1155-1160.
Plasma levels of angiotensin ii during different penile conditions
in the cavernous and systemic blood of healthy men and patients with
erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2001;58 (5).
Possible role of bradykinin and angiotensin ii in the regulation of
penile erection and detumescence. Urology. 2001;57 (1).
Dorrance AM, Lewis RW, Mills TM. Captopril treatment reverses erectile
dysfunction in male stroke prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int
J Impot Res. 2002 Dec;14(6):494-7.
Hamed EA, Meki AR, Gaafar AA, Hamed SA. Role of some vasoactive mediators
in patients with erectile dysfunction: their relationship with angiotensin-converting
enzyme and growth hormone. Int J Impot Res. 2003 Dec;15(6):418-25.
Virag R, Floresco J, Richard C. Impairment Of Shear-Stress-Mediated
Vasodilation Of Cavernous Arteries In Erectile Dysfunction. Int
J Impot Res. 2004 Jan;16(1):39-42.
Fibromyalgia
Preliminary Clinical Report of ECE Phase I-a Clinical
Trial Results,
November 25, 2005 (Manufacturer's Study).
Brain Support/Memory Enhancement
"Composition for Prevention and Improvement of Dementia and Promotion
of Memory, and Healthy Assistance Foodstuffs Containing the Composition." Korean
Patent Application# 10-2003-88177 (Assigned To Haengwoo Lee).
Lee BH, Stein S. "Improvement of Learning Behavior of Mice by
an Antiacetylcholinesterase and Neuroprotective Agent Nx42, A Laminariales-Alga
Extract" Presented to the Pharm. Soc. Kor., Spring Conference
(2004); Manuscript Submitted to Korean Journal
of Food Science and Technology.
Myung CS, Shin HC, Bao HY, Yeo SJ, Lee BH, Kang JS. Improvement of
memory by dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol in ethanol-treated mice:
possible involvement of the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. Arch
Pharm Res. 2005 Jun;28(6):691-8.
Tsukada H, Nishiyama S, Fukumoto D, Ohba H, Sato K, Kakiuchi T. Effects
of acute acetylcholinesterase inhibition on the cerebral cholinergic
neuronal system and cognitive function: functional imaging of the conscious
monkey brain using animal pet in combination with microdialysis. Synapse. 2004;52:1-10.
Arthritis/Neuralgia
Kang KJ, Hwang HJ, Hong DH, Park YJ, Kim SH, Lee BH, Shin HC. Anti-oxidant
and anti-inflammatory activities of ventol, a phlorotannin-rich natural
agent derived from ecklonia cava, and its effect on proteoglycan
degradation in cartilage explant culture. Submitted to Molecular
Pathology and Pharmacology.
Kim MM, Ta QV, Mendis E, Rajapakse N, Jung WK, Byun HG, Jeon YJ, Kim
SK. Phlorotannins in Ecklonia cava extract inhibit matrix metalloproteinase
activity. Life Sci. 2006 Sep 5;79(15):1436-43. Epub 2006 May 7.
Lee SH, Han SB, Baik JY. The influence of vnp intake on the symptoms
of osteoarthritis of the knee joint. Clinical Report by Department
of Orthopedic Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University Medical Center.
Mcever RP. Selectins: novel receptors that mediate leukocyte adhesion
during inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 1991;65:223-228.
Sheehan DC, Hrapchak BB. Connective Tissue/Muscle Fiber Stains. In
Theory And Practice Of Histotechnology. Columbus, Ohio: Battelle Press;
1980:180-201.
Shibata T, Fujimoto K, Nagayama K, Yamaguchi K, Nakamura, T. Inhibitory
activity of brown algal phlorotannins against hyaluronidase. Int.
J. Food Sci. Tech. 2002;37: 703-709.
Shibata T, Nagayama K, Tanaka R, Yamaguchi K, Nakamura T. Inhibitory
effects of brown algal phlorotannins on secretory phospholipase a2s,
lipoxygenases and cycloxygenases. J. Appl.
Phycol. 2003;15: 61-66.
Shin HC, Hwang HJ, Kang KJ, Lee BH. An antioxidative and antiinflammatory
agent for potential treatment of osteoarthritis from Ecklonia cava.
Arch Pharm Res. 2006 Feb;29(2):165-71.
Compound For Improving Neuralgia Containing Dibenzo-P-Dioxine Derivatives
Extracted From Marine Plants And Articles Comprising Thereof. Korean
Patent Application 10-2004-0028066 (Livechem, Inc)
Evaluation of SEANOL on the Relief Effects on Neuralgic Pain, Sep.
30, 2005 (Manufacturer's Study).
Weight Loss/DGAT Inhibition
Cases, et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. October 1998; 95:13018-13023.
Smith SJ, Cases S, Jensen DR, et al. Nat Genet.
2000;25:87-90.
Immune Support
Ahn MJ, Yoon KD, Min SY, Lee JS, Kim JH, Kim TG, Kim SH, Kim NG, Huh
H, Kim J. Inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and protease
by phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia cava. Biol Pharm
Bull. 2004 Apr;27(4):544-7.

Page 1, 2 Keywords: fibromyalgia, hypertension,
sexual and erectile dysfunction, memory enhancement, relaxation and
alertness, deep sleep, allergies, asthma
|



![]()
![]()
![]()



